Add / update / delete servers through ezeelogin API
How to add/delete/update servers in GUI using API calls via command-Line interface (CLI) and via web?
root@gateway:~# scp -r /usr/local/ezlogin/apilib /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi user@remoteserver:/var/www/html/
user@remoteserver:~# chmod +x /var/www/html/ezwapi.php
user@remoteserver:~# chown www-data:www-data /var/www/html/* -R
Add/Delete/Edit servers using the API
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php [params...]
Via web as:
https://gateway.eznoc.com/ezwapi.php [params...]
For Help
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help
Usage:
ezwapi.php -help <action>
action : API action (add_server/update_server/remove_server/reset_fingerprint/add_user_server_acl)
1. Add Server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help add_server
Usage:
ezwapi.php add_server -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -name <hostname> -description <description> -password <password> -ip_address <IP address> -group <group> [-ssh_port <port>] [-ssh_user <username>] [-keep_password <Y/N/S>]
[-enable_ssh <Y/N/H>] [-cp <control panel>]
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-name : The server host name
-description : A description for the server
-password : The server password
-ssh_key : The SSH private key file (optional)
-passphrase : The SSH key pass phrase (optional)
-ip_address : The server IP address
-ssh_port : The server SSH port (optional, use default if unspecified)
-ssh_user : The server SSH user (optional, use default if unspecified)
-switch_user : Switch to this user after login as SSH user (optional)
-switch_pass : Password for switch user (optional)
-switch_sudo : Y or N or E to escalate privilege with ’sudo su’ or ’enable’ (for Cisco devices) (optional, default: N = disabled)
-prompt1 : Unique string in shell prompt of SSH user (optional)
-prompt2 : Unique string in password prompt for su or sudo (optional, default: Password:)
-prompt3 : Unique string in shell prompt of root user (optional, required for sudo)
-group : The server group name
-keep_password : Y (keep given password), N (automatic) or S (keep server password as such - no verification) (optional, default: Y)
-enable_ssh : Y, N or H to enable/disable/via Host Node (optional, default: N)
-ishn : Y or N to make this a Host Node or not (optional, default: N)
-onhost : The name of Host Node (optional, default: N)
-cp : The control panel name (optional, use default if unspecified)
-dc : The datacenter name (optional, use default if unspecified)
-rc_host : The remote console host (optional)
-rc_user : The remote console user (optional)
-rc_pass : The remote console password (optional)
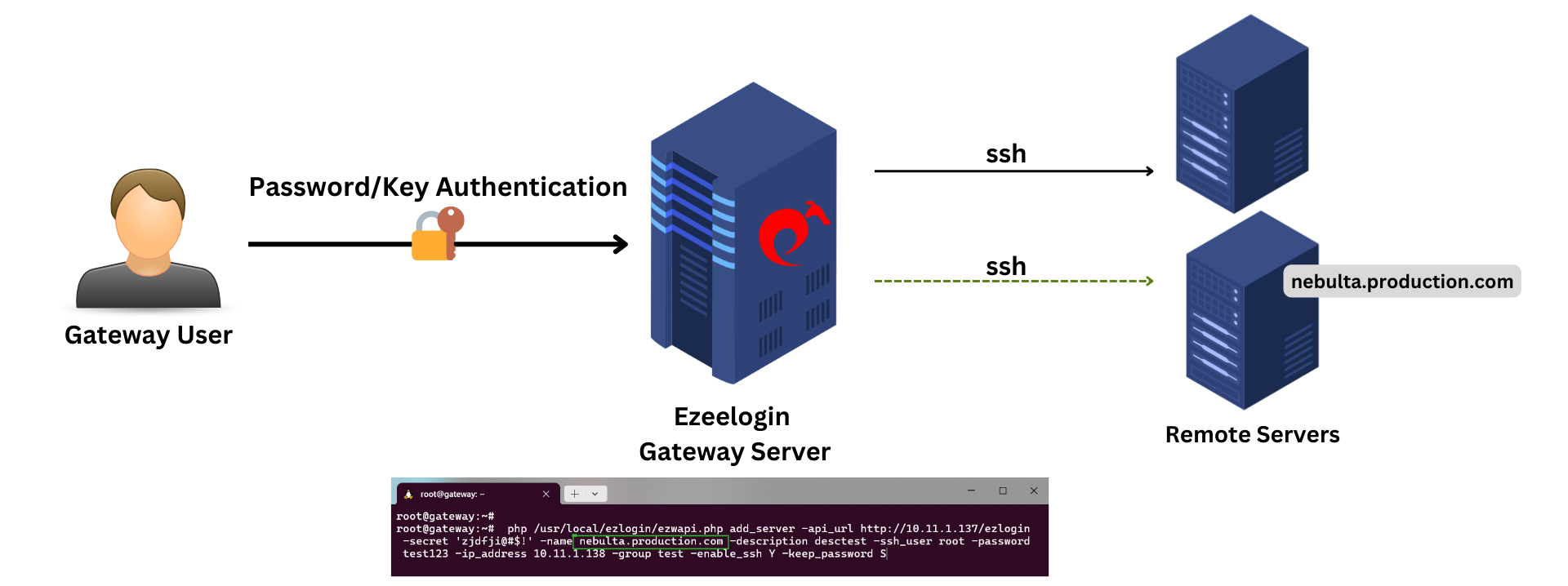
Step 1(A): The below example shows how to add a Server in GUI with the remote ssh user as ’root’
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php add_server -api_url http://10.11.1.137/ezlogin -secret 'zjdfji@#$!' -name test.noc.com -description desctest -ssh_user root -password test123 -ip_address 10.11.1.138 -group test -enable_ssh Y -keep_password S
Special characters password can be saved using API with single quotes.
eg: -password ’??r&5Q*gyKc6nGAE()’
Step 1(B): The example below shows how to add a server in GUI when the remote ssh user is non-privileged user ’admin’
How will I find the prompts for the ssh_user?
1. To find prompt1 ssh as the user directly into the server. The prompts may vary depending on the remote OS in use.
- For Centos 5,6,7
[admin@skunk ~]$ cd /home
Here prompt1 is "]$ "
- For Ubuntu 14,16 ,18
admin@ubu-nscd:~$ cd /home
Here the prompt1 is "~$ "
2. To find prompt2, simply run su - as a non root user.
[admin@skunk home]$ su -
Password:
Here prompt2 will be "ssword: "
3. The prompt 3 would be how the root prompt looks like
[root@skunk home]#
Above the unique characters that is permanent are "ot@sk" or "root@" etc.
2. Update Server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help update_server
Usage:
ezwapi.php update_server -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -name <hostname> [-newname <new hostname>] [-password <password>] [-ip_address <IP address>] [-ssh_port <port>] [-ssh_user <username>]
[-group <group>] [-keep_password <Y/N/S>] [-enable_ssh <Y/N>] [-cp <control panel>]
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-name : The server host name
-newname : The new host name (optional)
-description : A description for the server
-password : The server password (optional)
-ssh_key : The SSH private key file (optional)
-passphrase : The SSH key pass phrase (optional)
-ip_address : The server IP address (optional)
-ssh_port : The server SSH port (optional)
-ssh_user : The server SSH user (optional)
-switch_user : Switch to this user after login as SSH user (optional)
-switch_pass : Password for switch user (optional)
-switch_sudo : Y or N or E to escalate privilege with ’sudo su’ or ’enable’ (for Cisco devices) (optional, default: N = disabled)
-prompt1 : Unique string in shell prompt of SSH user (optional)
-prompt2 : Unique string in password prompt for su or sudo (optional)
-prompt3 : Unique string in shell prompt of root user (optional, required for sudo)
-rdp_port : The server RDP port (optional, use default if unspecified)
-group : The server group name
-keep_password : Y (keep given password), N (automatic) or S (keep server password as such - no verification) (optional)
-enable_ssh : Y, N or H to enable/disable/via Host Node (optional)
-ishn : Y or N to make this a Host Node or not (optional)
-onhost : The name of Host Node (optional)
-cp : The control panel name (optional)
-dc : The datacenter name (optional)
-rc_host : The remote console host (optional)
-rc_user : The remote console user (optional)
-rc_pass : The remote console password (optional)
Step 2(A): Refer below example to update the server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php update_server -api_url http://10.11.1.137/ezlogin -secret 'zjdfji@#$!' -name ez.test.com -description desctest -password test123 -ip_address 10.11.1.138 -group test -ssh_port 22 -rdp_port 3389
3. Delete Server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help remove_server
Usage:
ezwapi.php remove_server -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -name <hostname>
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-name : The server host name
Step 3(A) Refer below example to delete a server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php remove_server -api_url http://10.11.1.137/ezlogin -secret 'zjdfji@#$!' -name ez.test.com
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help list_servers
Usage:
ezwapi.php list_servers -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret>
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php list_servers -api_url http://192.168.1.38/ezlogin -secret 'zjdfji@#$!'
200: {"status":"success","extra":[{"id":"3","name":"db.eznoc.com"},{"id":"16","name":"Log.eznoc.com"},{"id":"17","name":"Production server"},{"id":"10","name":"Windows Server"}]}
Listing servers via API is only available from Ezeelogin version 7.40.0
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help reset_fingerprint
Usage:
ezwapi.php reset_fingerprint -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -name <hostname>
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-name : The server host name
Step 5(A): Refer below example to reset fingerprint for a remote server
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php reset_fingerprint -api_url http://192.168.29.4/ezlogin -secret 123456 -name Cent-database.hu
For multiple remote servers:
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php reset_fingerprint -api_url http://192.168.1.9/ezlogin -secret 'Admin@1234#' -name Develop_server Project_ubuntu Apiserver
200: {"status":"success","data":"SSH fingerprint has been cleared"}
6. User-server access control
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help add_user_server_acl
Usage:
ezwapi.php add_user_server_acl -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -user <username> -server <hostname> [-defer]
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-user : The username
-server : The server host name
-defer : Defer the ACL addition if user doesn’t already exist (optional)
Step 6(A): Refer below example for user-server access control
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php add_user_server_acl -api_url http://192.168.1.9/ezlogin -secret zxcvbnm -user victor -server centos.server
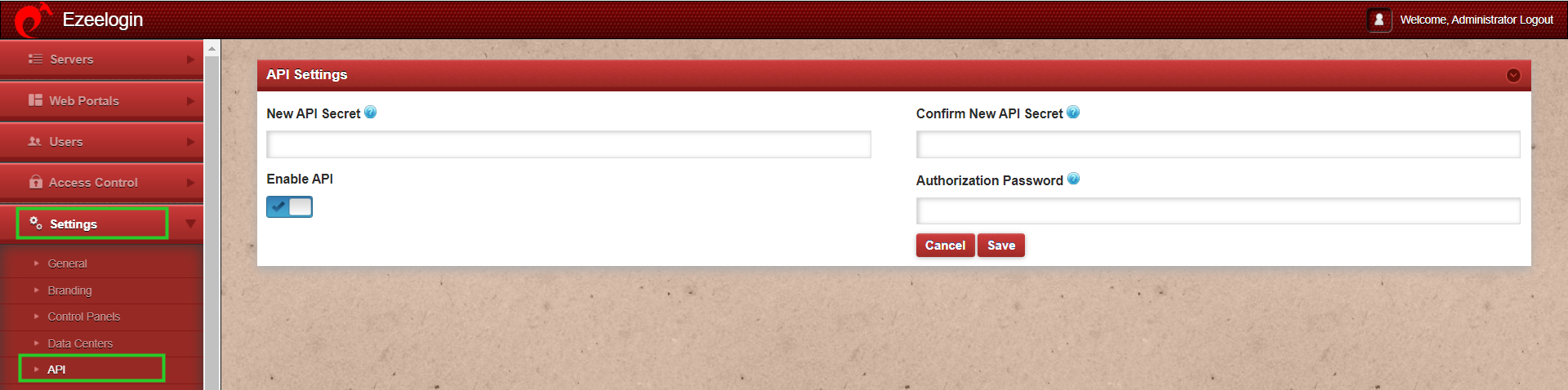
- Make sure API is enabled in API settings for the API script to work.
- If you need to execute the API script from a server other than the Ezeelogin installed server(jump server), copy /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php and /usr/local/ezlogin/apilib file to the server which you want to execute. PHP should be installed on the server.
7. Retrieve passwords of servers
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php -help get_password
Usage:
ezwapi.php get_password -api_url <API URL> -secret <API secret> -name <hostname(s)>
-api_url : The API URL
-secret : The API secret configured in web panel settings
-name : The server host name(s)
Step 7(A): Refer to the example below to retrieve password of a single server.
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php get_password -api_url http://192.168.0.140/ezlogin -secret 'Admin
!2345' -name db.eznoc.com
200: [{"name":"db.eznoc.com","id":"2","password":"root"}]
Step 7(B): Refer to the example below to retrieve password of multiple servers.
root@gateway:~# php /usr/local/ezlogin/ezwapi.php get_password -api_url http://192.168.1.9/ezlogin -secret 'Admin@1234#' -name db.eznoc.com dev.eznoc.com prod.eznoc.com
200: [{"name":"db.eznoc.com","id":"2","password":"root"},{"name":"dev.eznoc.com","id":"3","password":"admin@123"},{"name":"prod.eznoc.com","id":"1","password":"ubuntu@123"}]
This feature to retrieve passwords for both single and multiple servers are is available from Ezeelogin version 7.42.0
How to View API logs
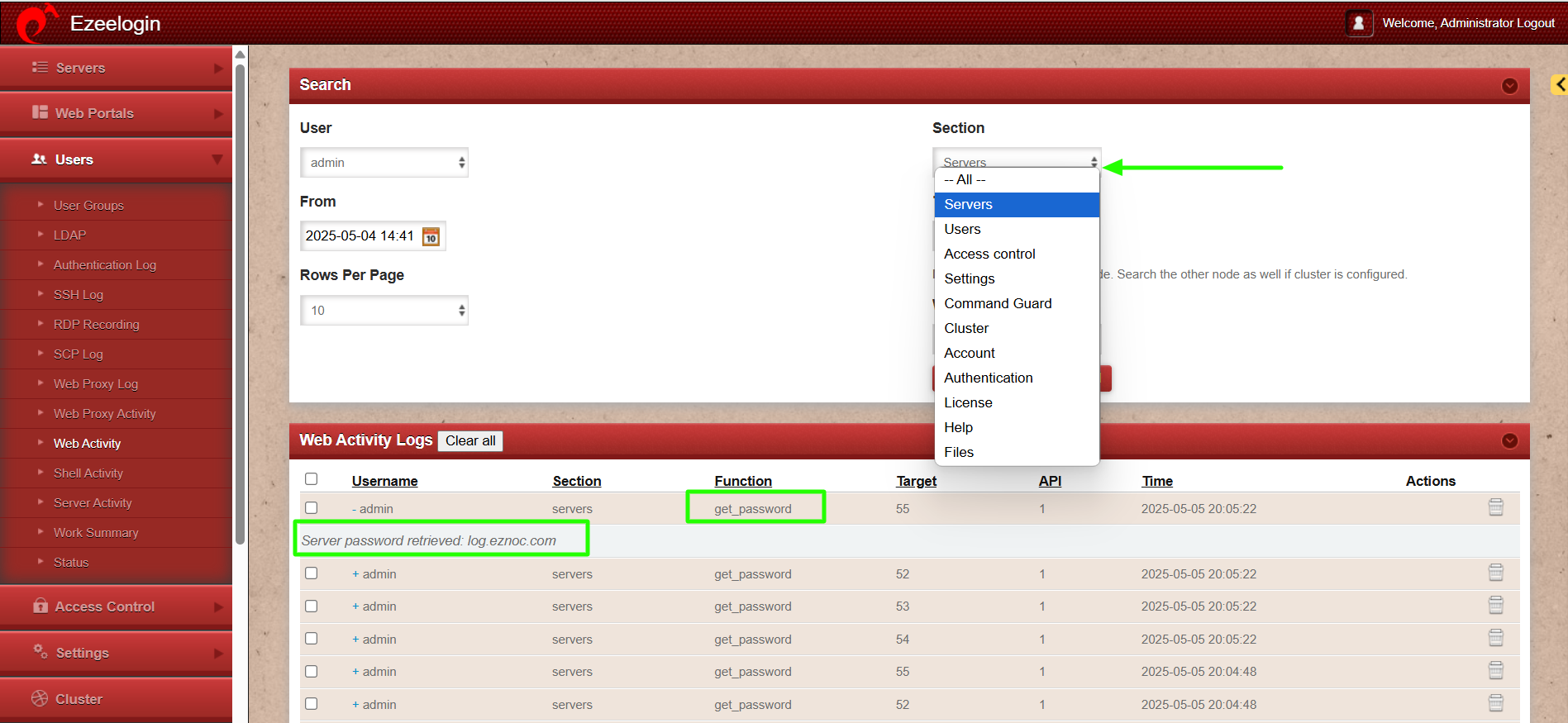
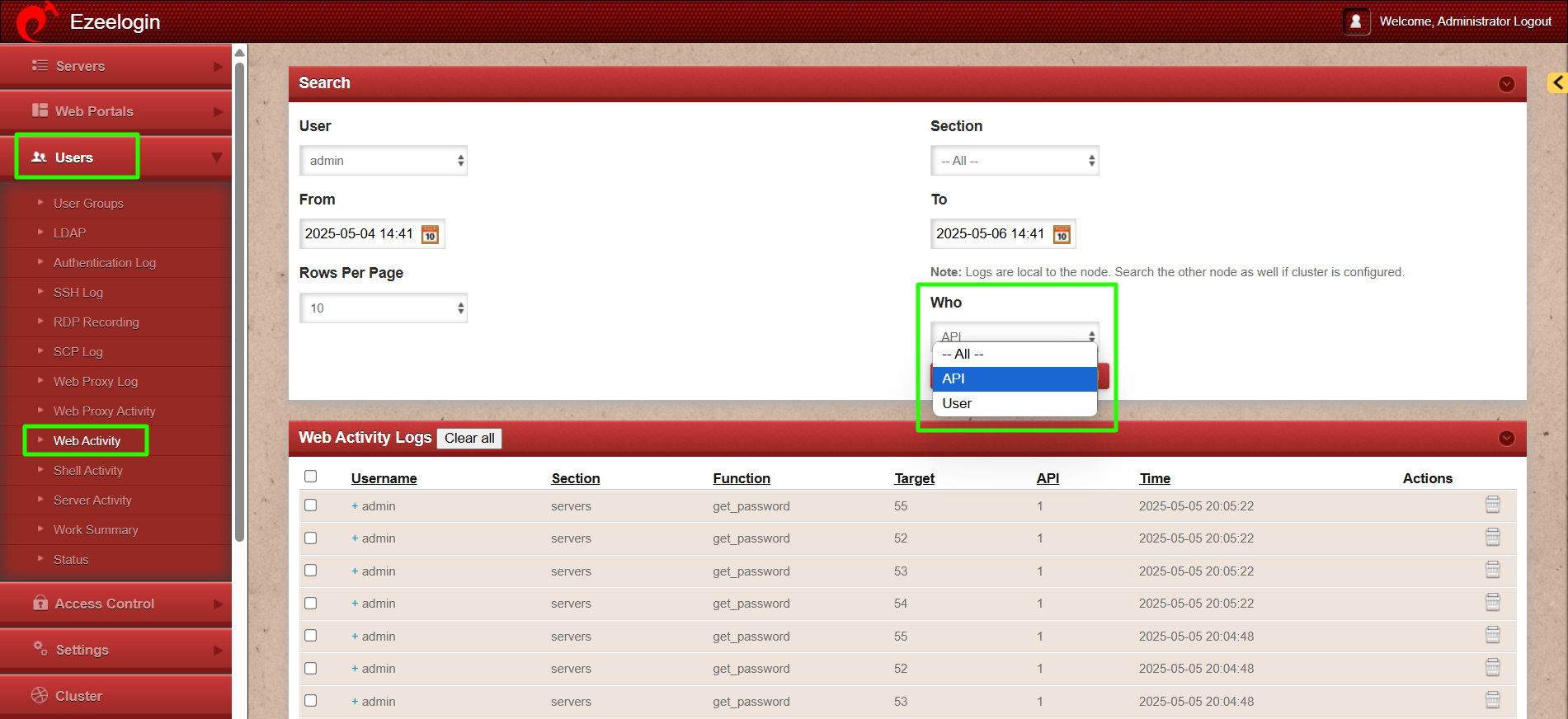
Step 1(A): To view all the actions performed via API navigate to Users -> Web Activity -> who and select API. This will display a list of logs for all the actions executed through API.
Step 1(B): From the drop-down menu for the section, select "Servers" which will display the list of logs for all servers whose passwords have been retrieved via API.